Typedefs | |
| typedef uint32_t | flashdata_t |
| typedef uintptr_t | flashaddr_t |
| Address in the flash memory. | |
| typedef uint8_t | flashsector_t |
| Index of a sector. | |
Functions | |
| size_t | flashSectorSize (flashsector_t sector) |
Get the size of sector. | |
| uintptr_t | getFlashAddrFirstCopy (void) |
| uintptr_t | getFlashAddrSecondCopy (void) |
| int | intFlashErase (flashaddr_t address, size_t size) |
Erase the sectors containing the span of size bytes starting at address. | |
| bool | intFlashIsErased (flashaddr_t address, size_t size) |
Check if the size bytes of flash memory starting at address are erased. | |
| bool | intFlashCompare (flashaddr_t address, const char *buffer, size_t size) |
Check if the data in buffer are identical to the one in flash memory. | |
| int | intFlashRead (flashaddr_t source, char *destination, size_t size) |
Copy data from the flash memory to a destination. | |
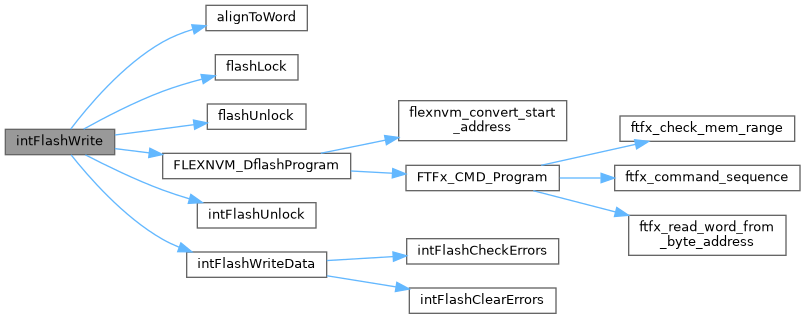
| int | intFlashWrite (flashaddr_t address, const char *buffer, size_t size) |
Copy data from a buffer to the flash memory. | |
Typedef Documentation
◆ flashaddr_t
| typedef uintptr_t flashaddr_t |
Address in the flash memory.
Definition at line 111 of file flash_int.h.
◆ flashdata_t
| typedef uint8_t flashdata_t |
Definition at line 64 of file flash_int.h.
◆ flashsector_t
| typedef uint8_t flashsector_t |
Index of a sector.
Definition at line 114 of file flash_int.h.
Function Documentation
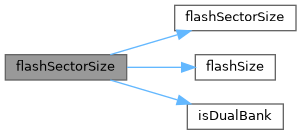
◆ flashSectorSize()
| size_t flashSectorSize | ( | flashsector_t | sector | ) |
Get the size of sector.
- Returns
sectorsize in bytes.
Definition at line 242 of file mpu_util.cpp.
Referenced by flashSectorSize(), intFlashSectorBegin(), and intFlashSectorErase().
◆ getFlashAddrFirstCopy()
| uintptr_t getFlashAddrFirstCopy | ( | void | ) |
Flex Non Volatile Memory is faster than flash It also has smaller pages so it takes less time to erase
There is no remote access to FlexNVM meaning that we cannot erase settings externally
Definition at line 253 of file mpu_util.cpp.
Referenced by getFlashAddrSecondCopy().


◆ getFlashAddrSecondCopy()
| uintptr_t getFlashAddrSecondCopy | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 257 of file mpu_util.cpp.
◆ intFlashCompare()
| bool intFlashCompare | ( | flashaddr_t | address, |
| const char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
Check if the data in buffer are identical to the one in flash memory.
- Parameters
-
address First address in flash memory to be checked. buffer Buffer containing the data to compare. size Size of bufferin bytes.
- Returns
- TRUE if the flash memory and the buffer contain identical data.
- FALSE if the flash memory and the buffer don't contain identical data.
Definition at line 109 of file flash_int.cpp.
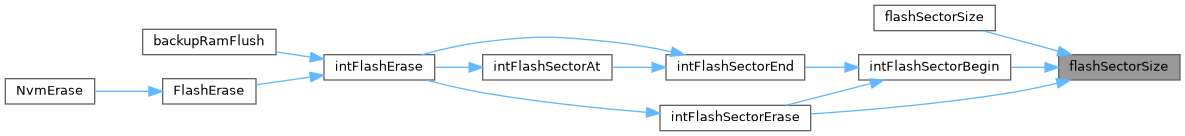
◆ intFlashErase()
| int intFlashErase | ( | flashaddr_t | address, |
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
Erase the sectors containing the span of size bytes starting at address.
- Warning
- If
addressdoesn't match the beginning of a sector, the data contained between the beginning of the sector andaddresswill be erased too. The same applies for data contained ataddress+sizeup to the end of the sector.
- Parameters
-
address Starting address of the span in flash memory. size Size of the span in bytes.
- Returns
- FLASH_RETURN_SUCCESS No error erasing the flash memory.
- FLASH_RETURN_BAD_FLASH Flash cell error.
- FLASH_RETURN_NO_PERMISSION Access denied.
Definition at line 115 of file flash_int.cpp.
Referenced by backupRamFlush(), and FlashErase().

◆ intFlashIsErased()
| bool intFlashIsErased | ( | flashaddr_t | address, |
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
Check if the size bytes of flash memory starting at address are erased.
- Note
- If the memory is erased, one can write data into it safely.
- Parameters
-
address First address in flash memory to be checked. size Size of the memory space to be checked in bytes.
- Returns
- TRUE Memory is already erased.
- FALSE Memory is not erased.
Definition at line 89 of file flash_int.cpp.
Referenced by FlashErase(), FlashVerifyChecksum(), and intFlashSectorErase().
◆ intFlashRead()
| int intFlashRead | ( | flashaddr_t | source, |
| char * | destination, | ||
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
Copy data from the flash memory to a destination.
- Warning
- The
destinationmust be at leastsizebytes long.
- Parameters
-
source First address of the flash memory to be copied. destination Buffer to copy to. size Size of the data to be copied in bytes.
- Returns
- FLASH_RETURN_SUCCESS if successfully copied.
Definition at line 130 of file flash_int.cpp.
Referenced by backupInit().
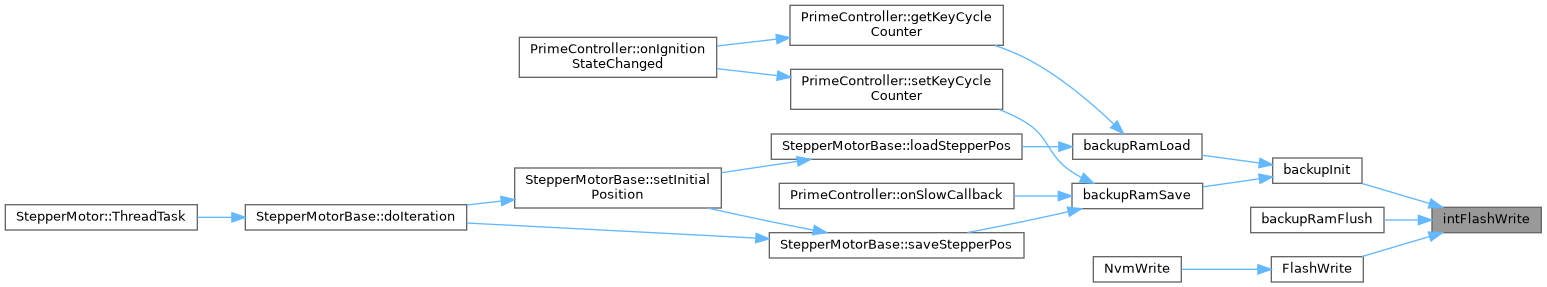
◆ intFlashWrite()
| int intFlashWrite | ( | flashaddr_t | address, |
| const char * | buffer, | ||
| size_t | size | ||
| ) |
Copy data from a buffer to the flash memory.
- Warning
- The flash memory area receiving the data must be erased.
-
The
buffermust be at leastsizebytes long.
- Parameters
-
address First address in the flash memory where to copy the data to. buffer Buffer containing the data to copy. size Size of the data to be copied in bytes.
- Returns
- FLASH_RETURN_SUCCESS No error.
- FLASH_RETURN_NO_PERMISSION Access denied.
Definition at line 443 of file flash_int.cpp.
Referenced by backupInit(), backupRamFlush(), FlashBufferFlush(), and FlashWrite().