Detailed Description
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct port_intctx | intctx_t |
Functions | |
| static void | reset_and_jump (void) |
| void | jump_to_bootloader () |
| void | jump_to_openblt () |
| BOR_Level_t | BOR_Get (void) |
| BOR_Result_t | BOR_Set (BOR_Level_t BORValue) |
| void | startWatchdog (int timeoutMs) |
| void | setWatchdogResetPeriod (int resetMs) |
| void | tryResetWatchdog () |
| uint32_t | getMcuSerial () |
| void | baseMCUInit () |
| int | getRemainingStack (thread_t *otp) |
| bool | isStm32F42x () |
| PUBLIC_API_WEAK void | boardPrepareForStop () |
| void | boardPreparePA0ForStandby () |
| PUBLIC_API_WEAK void | boardPrepareForStandby () |
| void | assertInterruptPriority (const char *func, uint8_t expectedPrio) |
Variables | |
| static efitimems_t | watchdogResetPeriodMs = 0 |
| static const efitimems_t | watchdogCounterResetDelay = 3000 |
| uint32_t | __main_stack_base__ |
Typedef Documentation
◆ intctx_t
| typedef struct port_intctx intctx_t |
Definition at line 213 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Function Documentation
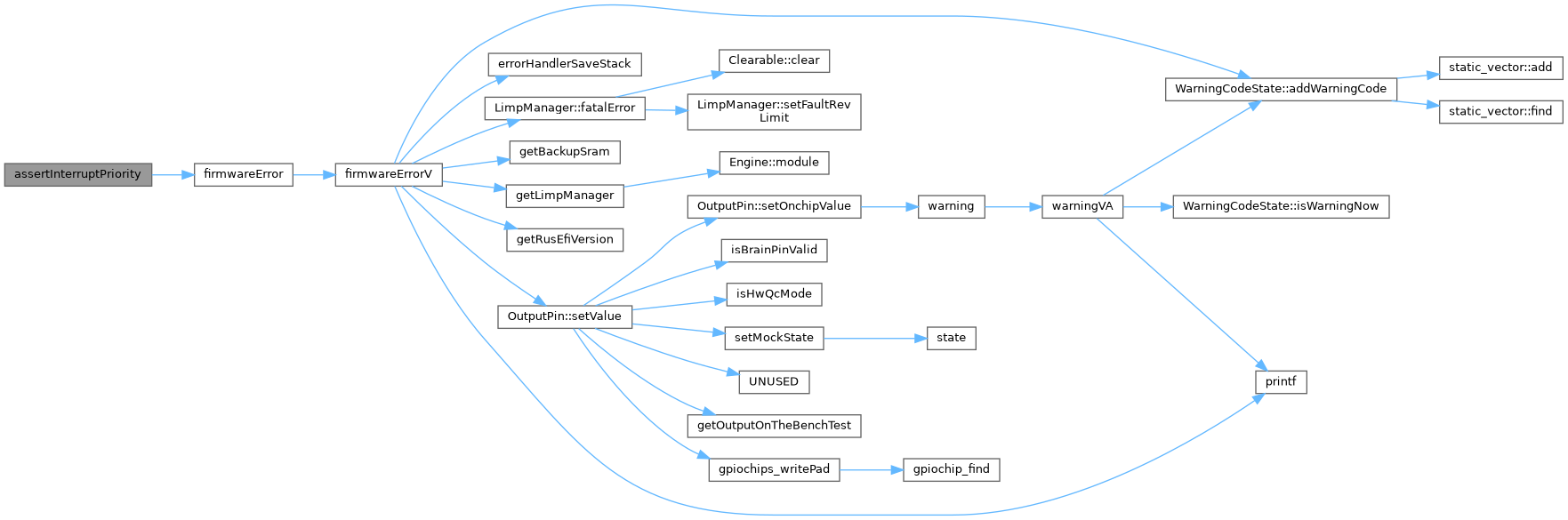
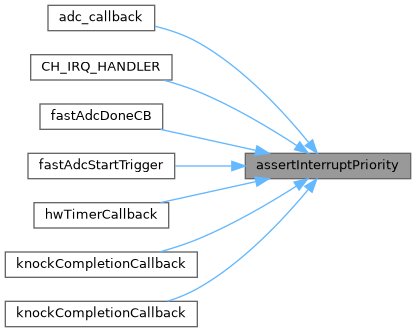
◆ assertInterruptPriority()
| void assertInterruptPriority | ( | const char * | func, |
| uint8_t | expectedPrio | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 284 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by adc_callback(), CH_IRQ_HANDLER(), fastAdcDoneCB(), fastAdcStartTrigger(), hwTimerCallback(), knockCompletionCallback(), and knockCompletionCallback().
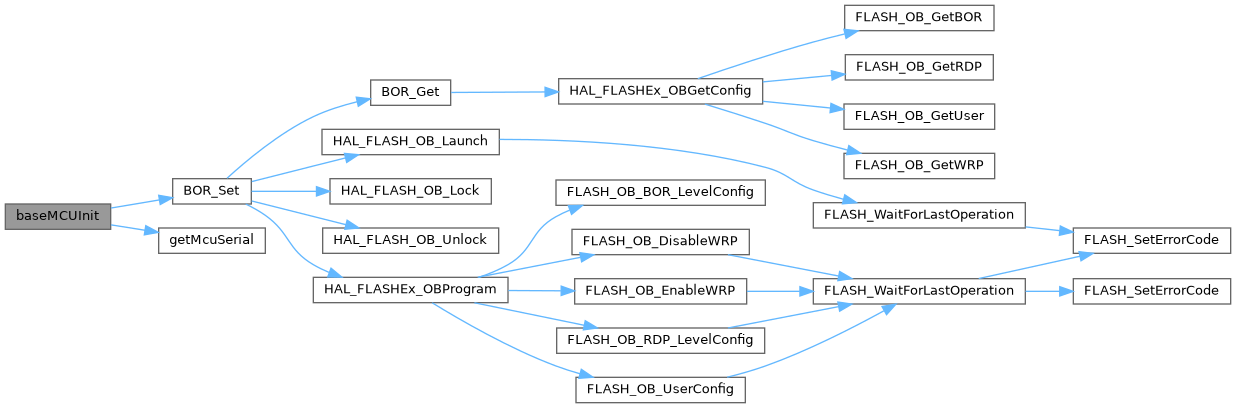
◆ baseMCUInit()
| void baseMCUInit | ( | ) |
Definition at line 195 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ boardPrepareForStandby()
| PUBLIC_API_WEAK void boardPrepareForStandby | ( | ) |
Definition at line 280 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by stm32_standby().


◆ boardPrepareForStop()
| PUBLIC_API_WEAK void boardPrepareForStop | ( | ) |
Definition at line 247 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ boardPreparePA0ForStandby()
| void boardPreparePA0ForStandby | ( | ) |
Standby uses special low power hardware - it always wakes on rising edge
Definition at line 256 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by boardPrepareForStandby().

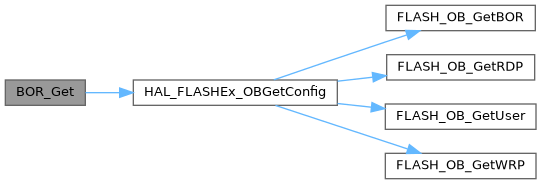
◆ BOR_Get()
| BOR_Level_t BOR_Get | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 86 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by BOR_Set().

◆ BOR_Set()
| BOR_Result_t BOR_Set | ( | BOR_Level_t | BORValue | ) |
Definition at line 96 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by baseMCUInit().
◆ getMcuSerial()
| uint32_t getMcuSerial | ( | ) |
Definition at line 190 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by baseMCUInit().
◆ getRemainingStack()
| int getRemainingStack | ( | thread_t * | otp | ) |
Of note is that interrupts are NOT serviced on the stack of the thread that was running when the interrupt occurred. The only thing that happens on that thread's stack is that its registers are pushed (by hardware) when an interrupt occurs, just before swapping the stack pointer out for the main stack (currently 0x400=1024 bytes), where the ISR actually runs. see also main_stack_size see also process_stack_size
see also http://www.chibios.org/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=chibios:kb:stacks
In the firmware we are using 'extern *Engine' - in the firmware Engine is a singleton
On the other hand, in order to have a meaningful unit test we are passing Engine * engine as a parameter
Definition at line 215 of file stm32_common.cpp.

◆ isStm32F42x()
| bool isStm32F42x | ( | void | ) |
Definition at line 238 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ jump_to_bootloader()
| void jump_to_bootloader | ( | ) |
Definition at line 63 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ jump_to_openblt()
| void jump_to_openblt | ( | ) |
Definition at line 72 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ reset_and_jump()
|
static |
Definition at line 39 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by jump_to_bootloader(), and jump_to_openblt().
◆ setWatchdogResetPeriod()
| void setWatchdogResetPeriod | ( | int | resetMs | ) |
Definition at line 160 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ startWatchdog()
| void startWatchdog | ( | int | timeoutMs | ) |
Definition at line 122 of file stm32_common.cpp.
◆ tryResetWatchdog()
| void tryResetWatchdog | ( | ) |
Definition at line 167 of file stm32_common.cpp.

Variable Documentation
◆ __main_stack_base__
|
extern |
Referenced by getRemainingStack().
◆ watchdogCounterResetDelay
|
static |
Definition at line 158 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by tryResetWatchdog().
◆ watchdogResetPeriodMs
|
static |
Definition at line 156 of file stm32_common.cpp.
Referenced by setWatchdogResetPeriod(), and tryResetWatchdog().