Functions | |
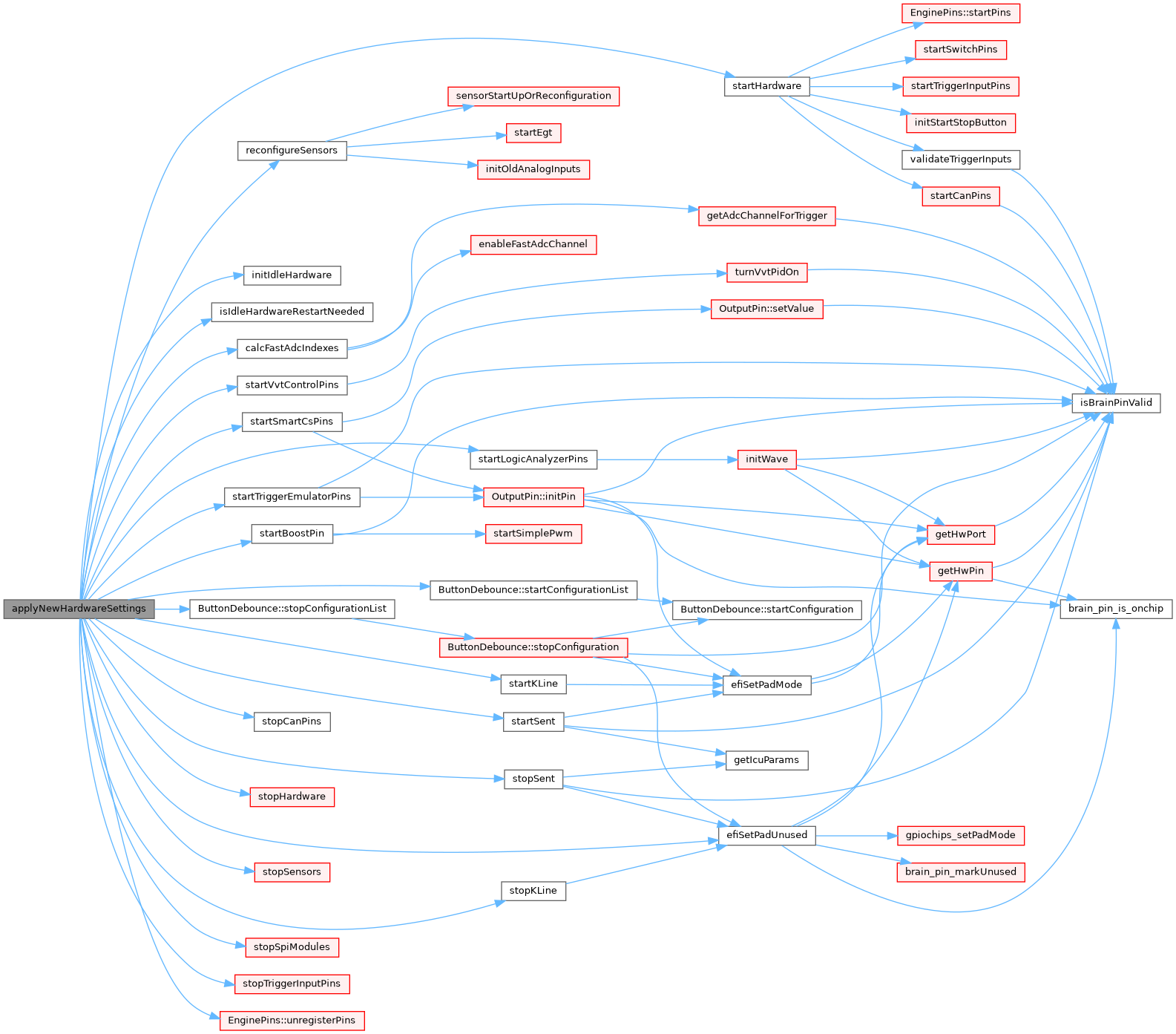
| void | startHardware () |
| void | stopHardware () |
| SPIDriver * | getSpiDevice (spi_device_e spiDevice) |
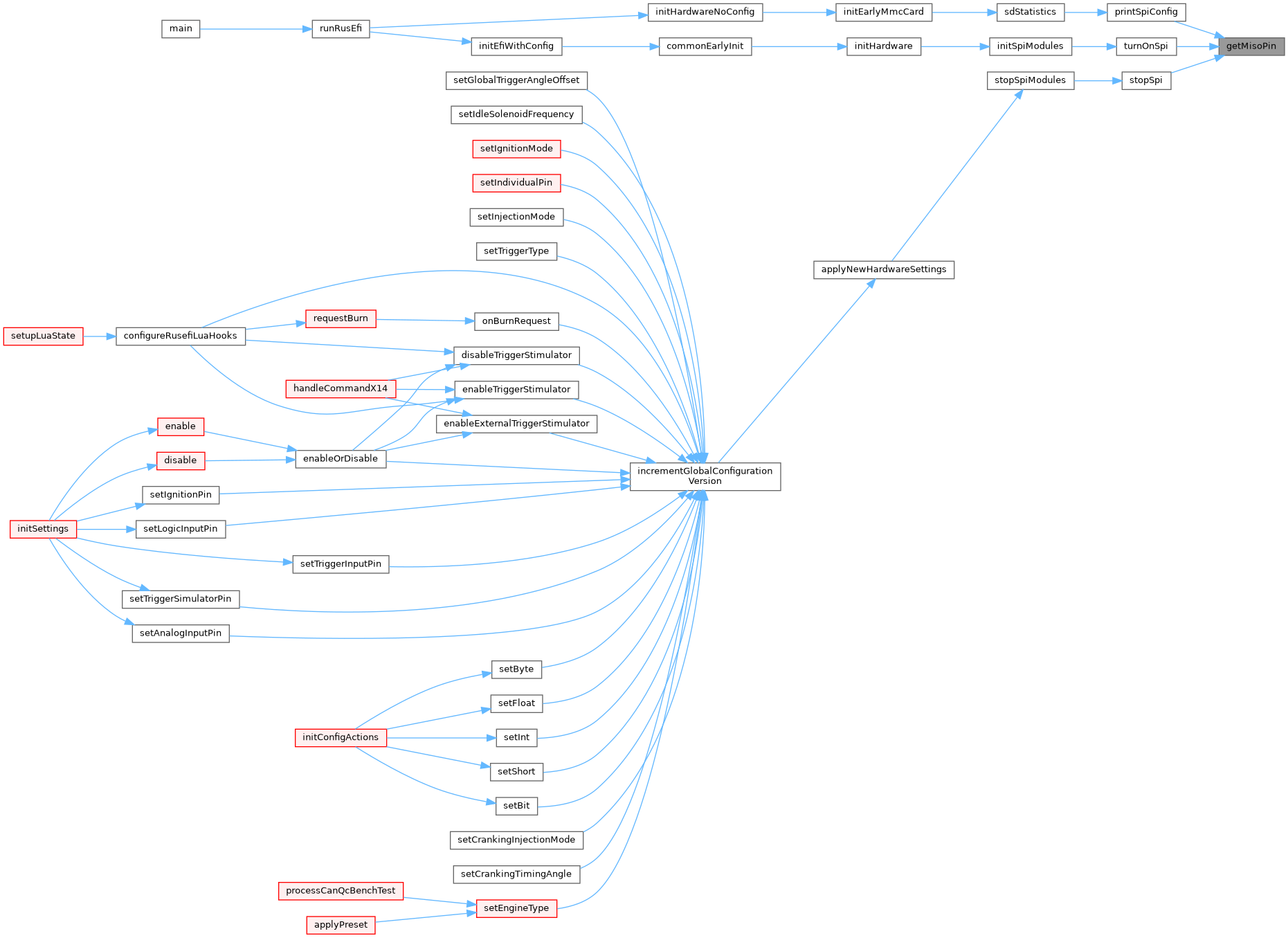
| void | turnOnSpi (spi_device_e device) |
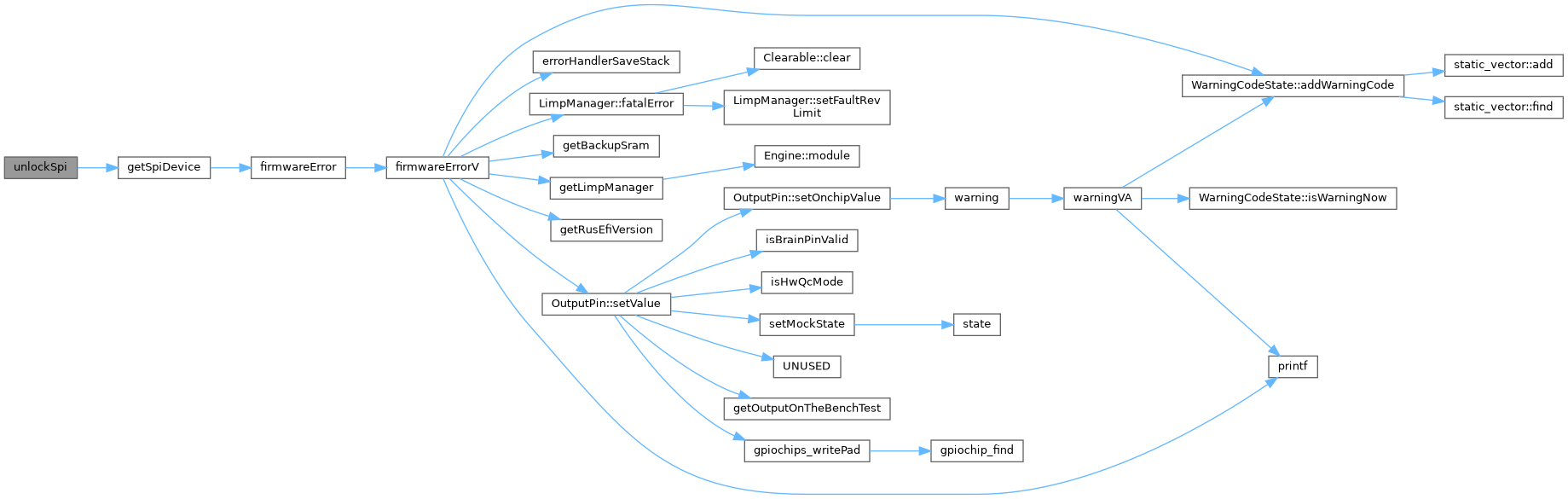
| void | lockSpi (spi_device_e device) |
| void | unlockSpi (spi_device_e device) |
| brain_pin_e | getMisoPin (spi_device_e device) |
| brain_pin_e | getMosiPin (spi_device_e device) |
| brain_pin_e | getSckPin (spi_device_e device) |
| void | printSpiConfig (const char *msg, spi_device_e device) |
| void | onFastAdcComplete (adcsample_t *) |
| void | applyNewHardwareSettings () |
| void | initHardwareNoConfig () |
| void | initHardware () |
| void | setBor (int borValue) |
Function Documentation
◆ applyNewHardwareSettings()
| void applyNewHardwareSettings | ( | ) |
this method is NOT currently invoked on ECU start todo: reduce code duplication by moving more logic into startHardware method
All 'stop' methods need to go before we begin starting pins.
We take settings from 'activeConfiguration' not 'engineConfiguration' while stopping hardware. Some hardware is restart unconditionally on change of parameters while for some systems we make extra effort and restart only relevant settings were changes.
Definition at line 314 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by incrementGlobalConfigurationVersion().
◆ getMisoPin()
| brain_pin_e getMisoPin | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Definition at line 89 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by printSpiConfig(), stopSpi(), and turnOnSpi().
◆ getMosiPin()
| brain_pin_e getMosiPin | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Definition at line 109 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by printSpiConfig(), stopSpi(), and turnOnSpi().
◆ getSckPin()
| brain_pin_e getSckPin | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Definition at line 129 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by printSpiConfig(), stopSpi(), and turnOnSpi().
◆ getSpiDevice()
| SPIDriver * getSpiDevice | ( | spi_device_e | spiDevice | ) |
- Returns
- NULL if SPI device not specified
Definition at line 152 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by initAccelerometer(), initializeMmcBlockDevice(), initPotentiometers(), initSmartGpio(), lockSpi(), nm_bus_init(), and unlockSpi().
◆ initHardware()
| void initHardware | ( | ) |
Definition at line 540 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by commonEarlyInit().

◆ initHardwareNoConfig()
| void initHardwareNoConfig | ( | ) |
histograms is a data structure for CPU monitor, it does not depend on configuration
We need the LED_ERROR pin even before we read configuration
Definition at line 430 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by runRusEfi().

◆ lockSpi()
| void lockSpi | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Only one consumer can use SPI bus at a given time
Definition at line 193 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by sendToPot().

◆ onFastAdcComplete()
| void onFastAdcComplete | ( | adcsample_t * | ) |
This method is not in the adc* lower-level file because it is more business logic then hardware.
this callback is executed 10 000 times a second, it needs to be as fast as possible
Definition at line 278 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by adc_callback(), and fastAdcDoneCB().
◆ printSpiConfig()
| void printSpiConfig | ( | const char * | msg, |
| spi_device_e | device | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 259 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by sdStatistics().

◆ setBor()
| void setBor | ( | int | borValue | ) |
Definition at line 412 of file hardware.cpp.
◆ startHardware()
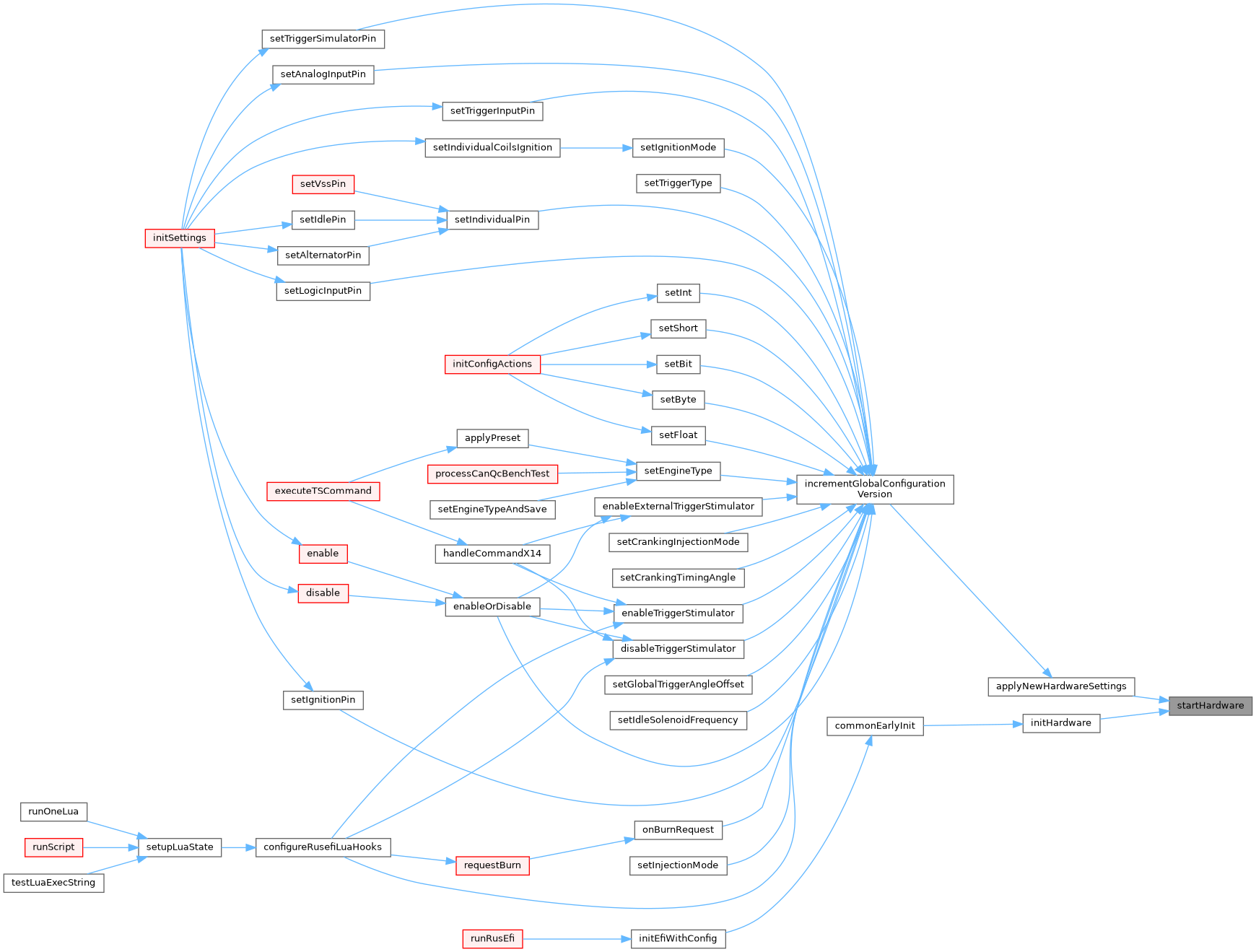
| void startHardware | ( | ) |
This method is invoked both on ECU start and configuration change At the moment we have too many system which handle ECU start and configuration change separately TODO: move move hardware code here
Definition at line 505 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by applyNewHardwareSettings(), and initHardware().
◆ stopHardware()
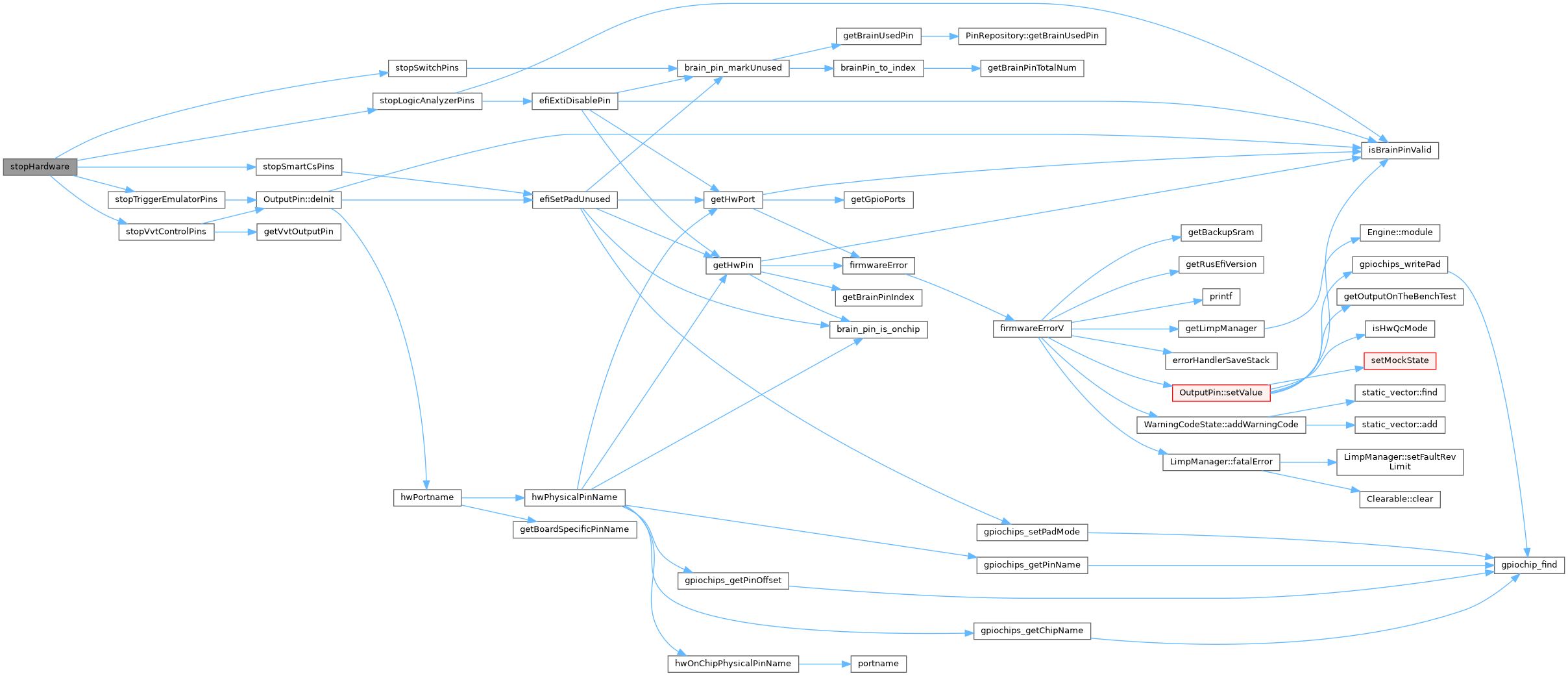
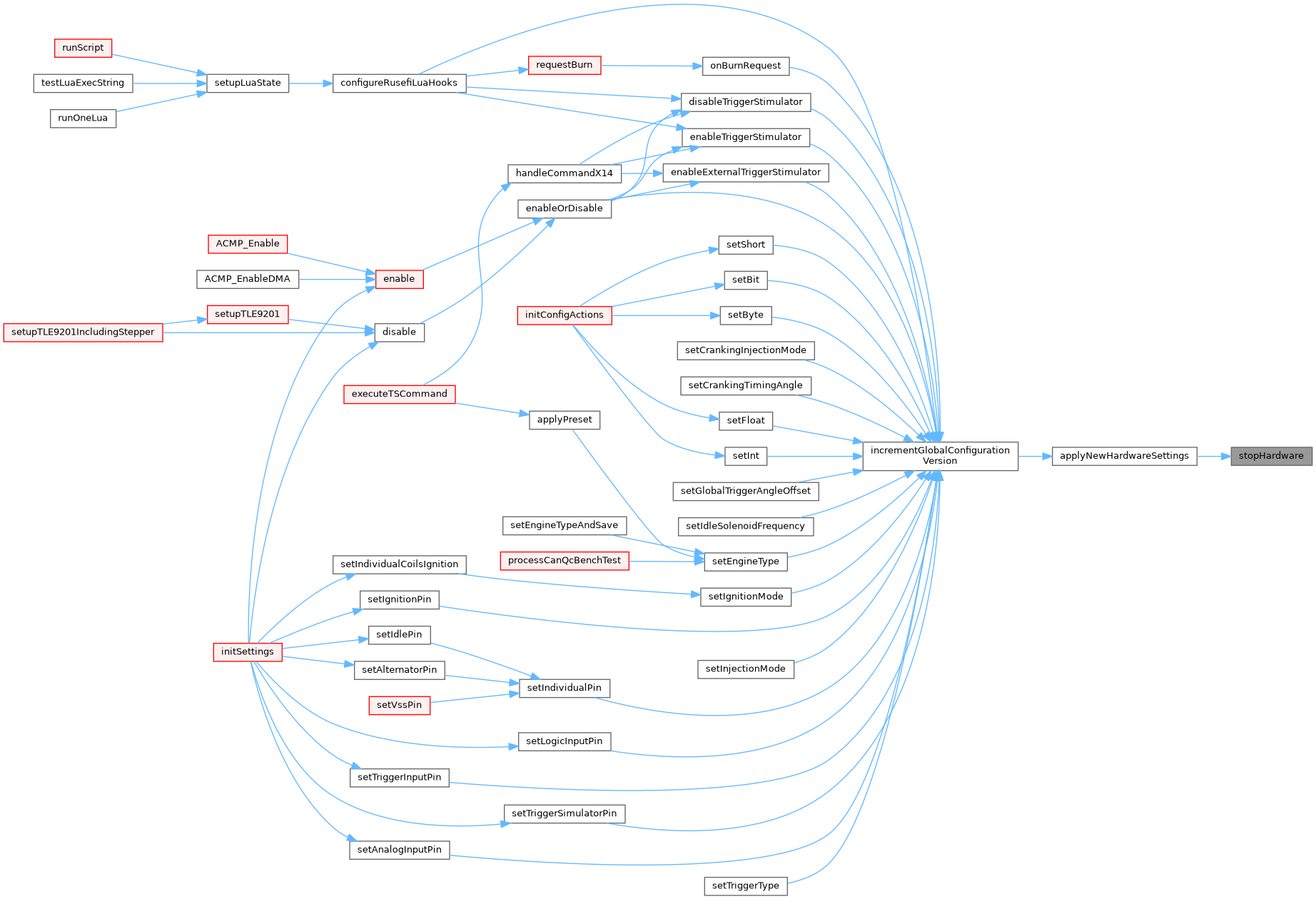
| void stopHardware | ( | ) |
Definition at line 480 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by applyNewHardwareSettings().
◆ turnOnSpi()
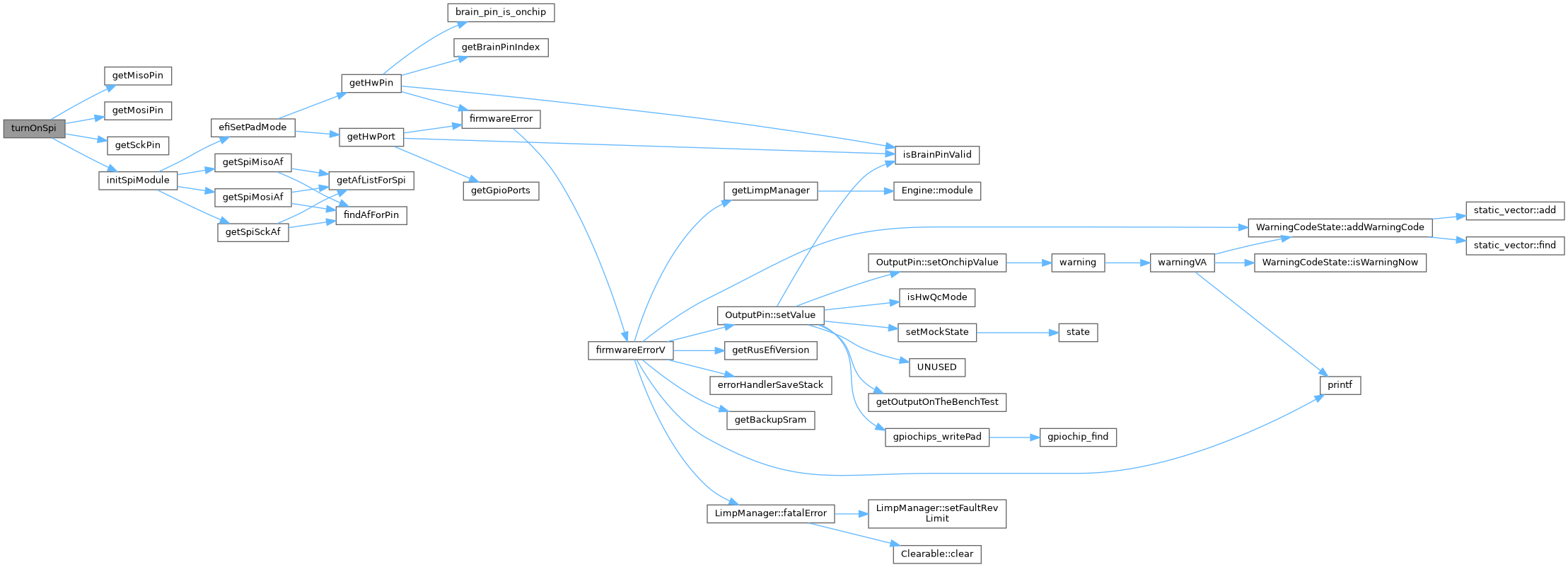
| void turnOnSpi | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Definition at line 151 of file at32_spi.cpp.
Referenced by initSpiModules().

◆ unlockSpi()
| void unlockSpi | ( | spi_device_e | device | ) |
Definition at line 198 of file hardware.cpp.
Referenced by sendToPot().